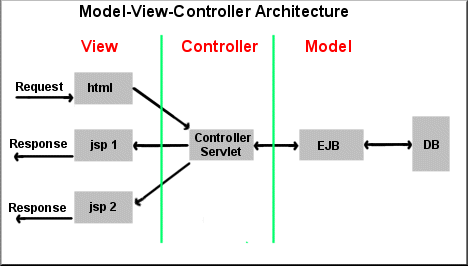
The goal of the Model-View-Controller (Model 2) framework is to separate the application object (model) from
the way it is represented to the user (view) from the way in which the user controls it (controller).
In J2EE the MVC framework approach adheres to the following:
- The controller translates interactions with the view into actions
to be performed by the model. In J2EE the controller would be represented by servlets.
- The model represents enterprise data and business rules that
govern access to and updates to this data. In J2EE the model would be
represented by JavaBeans or EJBs
- The view represents the user interface. In J2EE the views would be represented
by JSPs containing only presentation constructs (ie., no Java code).
|
